As professionals working in education, it's hard to imagine doing research without scholarly publications. Personnel located at any one of the Minnesota State colleges and universities have access to that institution's library-provided subscriptions. Due to complicated licensing and cost issues, that option is currently not available for system office personnel.
So. What can we do about that?
This guide provides information about resources that anyone who lives and/or works in the state of Minnesota can access, thanks to legislative funding and support from a combination of your local public library, MN Office of Higher Education (OHE), State Library Services in the MN Department of Education (MDE), and Minitex. Many of the resources in the databases are likely journals you are familiar with and have used in past research.
The tabs across the top of the screen are sorted into sources of information. Each tab provides information about that resource as well as instructions to access it.
- Quick Start is for those of you who just want to get started.
- eLibraryMN is a collection of 55 databases that contain primarily full-text electronic journal articles, newspapers, and other types of resources.
- MNLINK is a statewide system that serves as a discovery and interlibrary loan interface for library users and information seekers. This service handles both electronic and print resources.
I'm happy to help you track down resources or navigate the various libraries in Minnesota. And, any feedback on the usefulness of this guide would be great as well.
Email me at johnna.horton@mnsu.edu
Email me at johnna.horton@mnsu.edu

Johnna Horton is the Executive Director of PALS, a department that supports Minnesota State libraries and reports to Dr. Kim Lynch, Associate Vice Chancellor for Educational Development and Technology.
This section assumes you just want to dive in and find things.
The databases linked to the right are part of a list of 59 databases made available through public funding.
Looking for information other than what is listed on this tab? MNLINK https://mnlink.org/ will connect you to libraries throughout the state and provide access to their collections.
The MNLINK tab on this guide will help you navigate that resource.
The databases linked to the right are part of a list of 59 databases made available through public funding.
Looking for information other than what is listed on this tab? MNLINK https://mnlink.org/ will connect you to libraries throughout the state and provide access to their collections.
The MNLINK tab on this guide will help you navigate that resource.
While still on the article citation screen in the ELM database, use the options on the right to email the citation to yourself and then refer to the instructions in the MNLINK tab at the top of this guide to continue your search. These are separate systems, so you'll have to recreate your search in MNLINK.
If ELM doesn't have the journal you want, remember the title (and the publisher, if possible) and refer to the instructions in the MNLINK tab at the top of this guide.
If ELM doesn't have the journal you want, remember the title (and the publisher, if possible) and refer to the instructions in the MNLINK tab at the top of this guide.
- Broad academic scope:
- Academic Search Premier: Good starting place for many topics because it includes thousands of scholarly publications across all academic disciplines.
- Academic Search Premier: Good starting place for many topics because it includes thousands of scholarly publications across all academic disciplines.
- Education-specific databases:
- ERIC: Contains thousands of education-related articles within the professional literature.
- Professional Development Collection: Education journals and reports of interest to professional educators, researchers, and librarians.
- Minnesota Digital Library: Collection of images and documents from historical societies, public libraries, special archives, universities, and colleges that depict the history of Minnesota.
"eLibraryMN gives Minnesota residents access to magazine, journal, newspaper and encyclopedia articles, media, including images, videos, and audio files, and other information resources." --from https://elibrarymn.org/about#what
eLibraryMN is the most effective way to access a wide variety of research resources for people unaffiliated with a university or college, a condition that usually applies to Minnesota State system office personnel, as well as some of our K-12 and workforce partners.
*eLibraryMN is also referred to as ELM and will be used interchangeably in this guide as well as on the eLibraryMN webpage.
eLibraryMN is the most effective way to access a wide variety of research resources for people unaffiliated with a university or college, a condition that usually applies to Minnesota State system office personnel, as well as some of our K-12 and workforce partners.
*eLibraryMN is also referred to as ELM and will be used interchangeably in this guide as well as on the eLibraryMN webpage.
eLibraryMN is very effective when you know which database, ebook, or specific journal you'd like to access. For help using eLibraryMN, click on Learning Center on the homepage. There, you'll find instructional guides, help creating permanent links to content, and other research assistance.
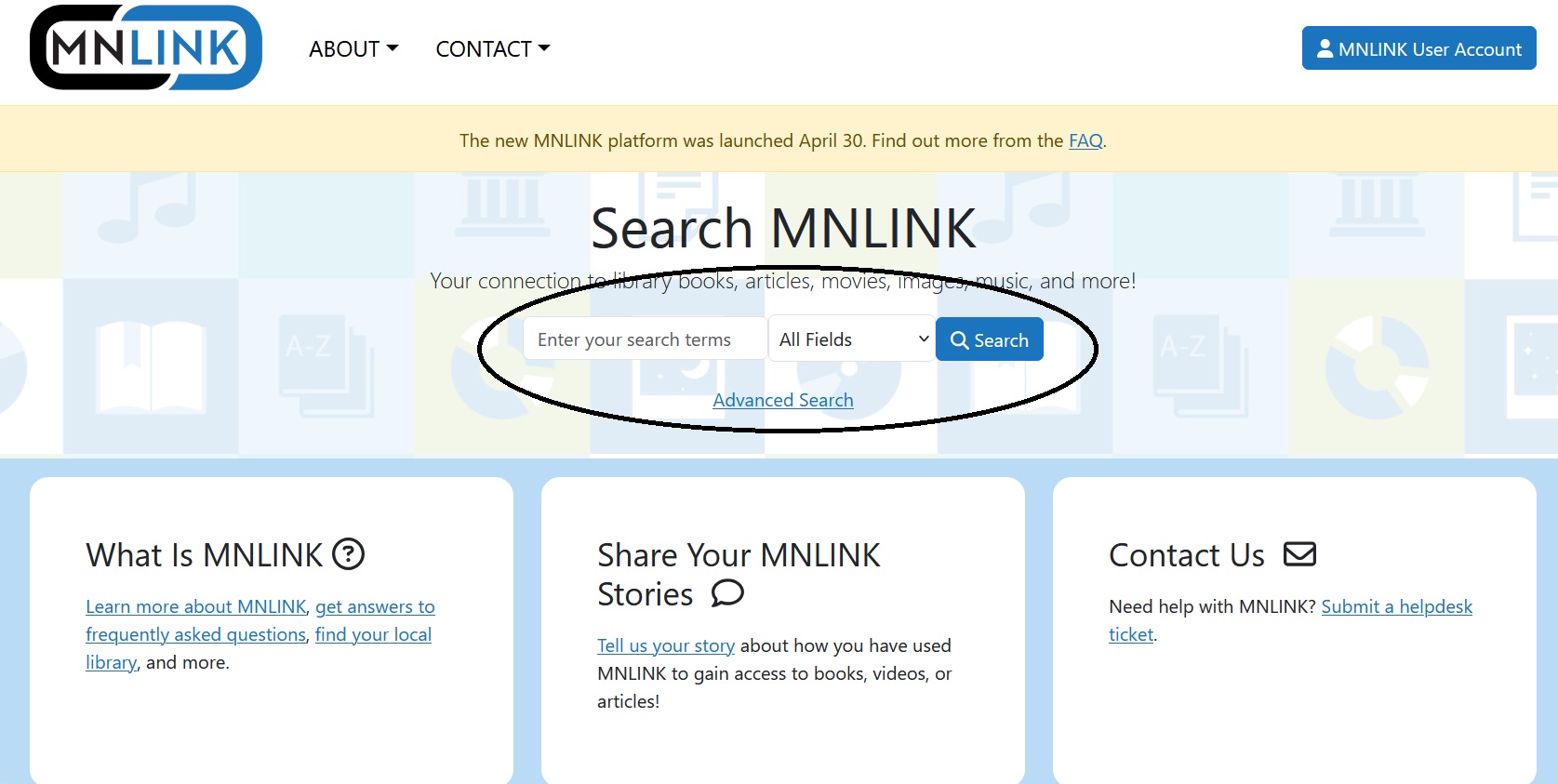
https://elibrarymn.org/ is the URL for eLibraryMN. On that page (see image below) you'll have several options for browsing, including the very useful Topic Search that helps you narrow your possible databases as well as a Find a Publication box where you can search for specific journals.
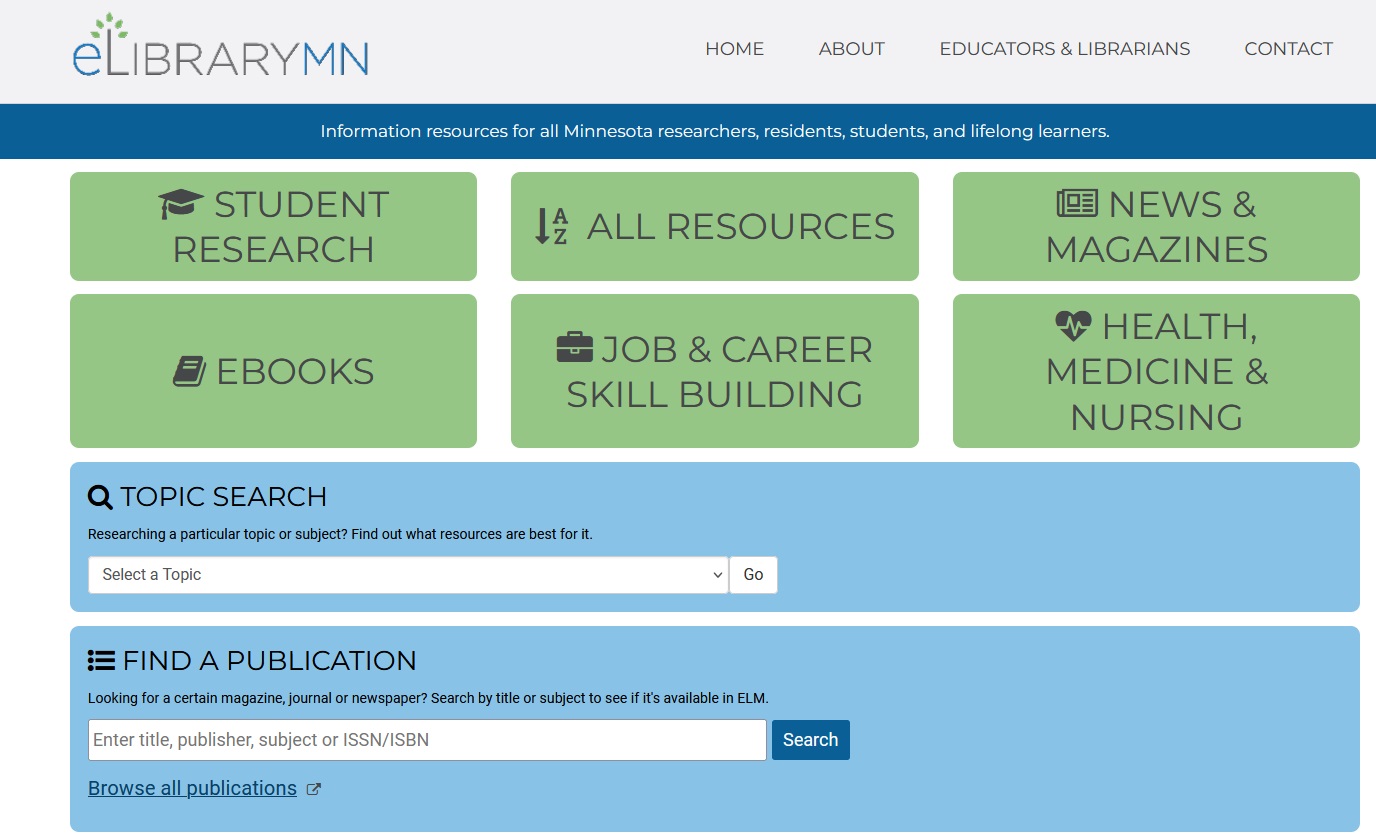

On the home screen, if you don't have a particular journal/publication in mind, I recommend clicking on Browse all publications (the link under the Find a Publication search box) to get to this screen where you can choose to browse by name or subject.
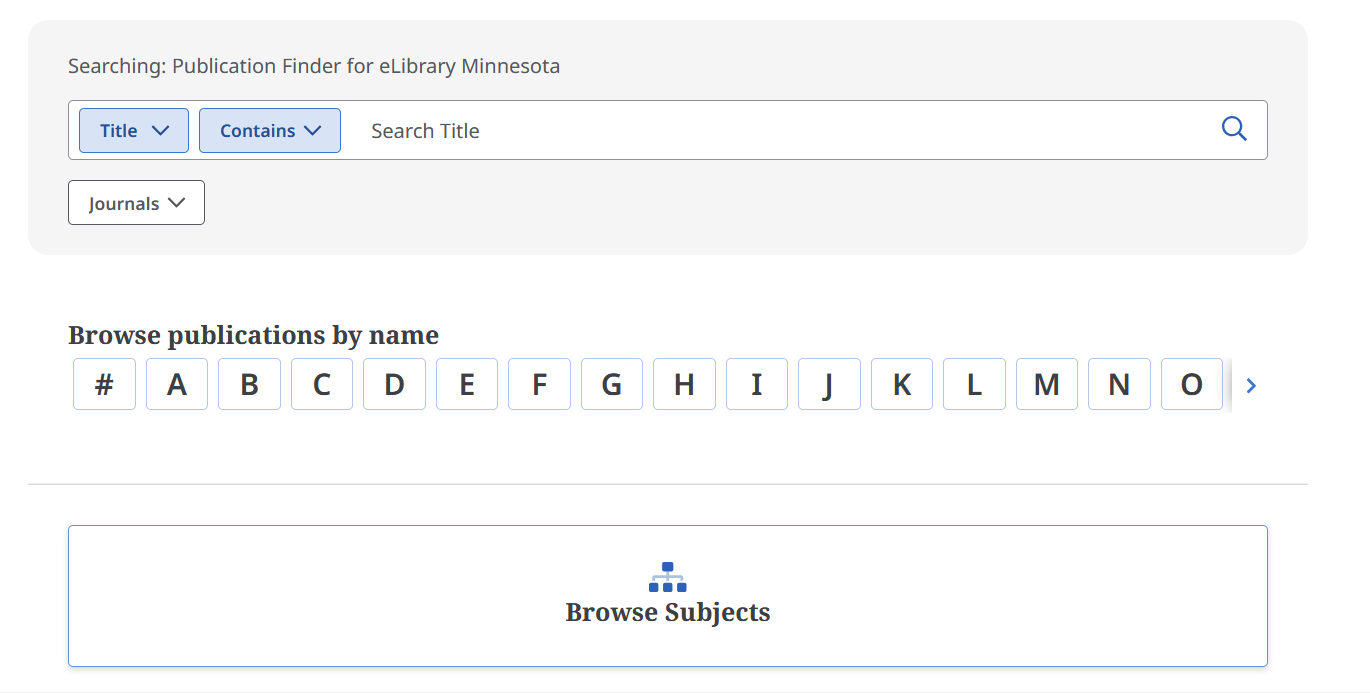
In this case, I will choose Browse Subjects, which leads to a list that has expandable terms:

On the left, you'll see options to refine your search. Once you've located the journal you're interested in, click the title, and you'll have links to access the journal.
Click on a database link (Academic Search Premier is always a good option) and you'll be taken to more detailed information, including a complete listing of the journal's contents on the right side of the screen. They are sorted by year, and then by issue.

In this case, I will choose Browse Subjects, which leads to a list that has expandable terms:

On the left, you'll see options to refine your search. Once you've located the journal you're interested in, click the title, and you'll have links to access the journal.
Click on a database link (Academic Search Premier is always a good option) and you'll be taken to more detailed information, including a complete listing of the journal's contents on the right side of the screen. They are sorted by year, and then by issue.
If you refined your results to "Full Text" when you started browsing articles, you should be able to click to view the article. Below, this article has two options for viewing- HTML and PDF Full Text.


While still on the article citation screen, use the options on the right to email the citation to yourself and then refer to the instructions in the MNLINK tab at the top of this guide to continue your search.
If ELM doesn't have the journal you want, remember the title (and the publisher, if possible) and refer to the instructions in the MNLINK tab at the top of this guide.
If ELM doesn't have the journal you want, remember the title (and the publisher, if possible) and refer to the instructions in the MNLINK tab at the top of this guide.
"MNLINK is a statewide system that serves as a discovery and interlibrary loan interface for library patrons and staff. Through our participating libraries, patrons have easy access to the catalogs of most libraries in Minnesota. The system also provides access to electronic resources that are available to Minnesotans. This includes electronic journals, images, and ebooks as well as access to the physical books that are held in libraries." --from https://mnlink.org/about/
MNLINK is useful when looking for articles that aren't available through ELM and physical items including books and copies of journal articles not in electronic format.
If you have a specific title, type the title into the basic search bar and use the drop down to select Title, or use the Advanced Search on the right of the screen.
This record is of a book I found while searching for recent items in "student services"

If I scroll down the page, I can see that two libraries in the state own this book, and I can request it to be sent to my public library:

If I'm NOT a member of either of these libraries, I can request this by clicking on the blue Request button and finding the library system where I have a library card, and entering the Library Barcode and PIN/Password so I can pick it up from my library.
This record is of a book I found while searching for recent items in "student services"

If I scroll down the page, I can see that two libraries in the state own this book, and I can request it to be sent to my public library:

If I'm NOT a member of either of these libraries, I can request this by clicking on the blue Request button and finding the library system where I have a library card, and entering the Library Barcode and PIN/Password so I can pick it up from my library.
This login page requires a library barcode and a PIN or password. If you don't have a public library card, now's a good time to get one! Each public library has information about obtaining a library card on their website.

Then, the Request form appears on the next screen and auto-populates important information (hopefully!). If there's enough info there including Author, Title, Journal, Date, Volume/Issue, and Pages, then just click the button that says Request. There is one at the top of the page and one at the bottom. Both work the same.
If you're requesting a journal article, it will more than likely be sent to your email in a few days. If you requested a physical item, you'll receive a notification from your public library (or other library you're affiliated with) when it's ready to be picked up.

Then, the Request form appears on the next screen and auto-populates important information (hopefully!). If there's enough info there including Author, Title, Journal, Date, Volume/Issue, and Pages, then just click the button that says Request. There is one at the top of the page and one at the bottom. Both work the same.
If you're requesting a journal article, it will more than likely be sent to your email in a few days. If you requested a physical item, you'll receive a notification from your public library (or other library you're affiliated with) when it's ready to be picked up.
Not sure if your library participates in MNLINK? Look that up here: https://mnlink.org/about/libraries
"Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. From one place, you can search across many disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions, from academic publishers, professional societies, online repositories, universities and other web sites. Google Scholar helps you find relevant work across the world of scholarly research." --from https://scholar.google.com/intl/en/scholar/about.html
You can use Google Scholar at any point in your process. I find it helpful when I'm trying to get an idea of what might be recently published in a particular subject area or when I'm struggling to find the right terms.
Google Scholar shouldn't be the only place you search. This resource explains why.
One aspect of Google Scholar that is important to note: Google Scholar links out to various repositories, many that are legal, and some that aren't. There may be some ethical decisions to make when conducting your research primarily in Google Scholar. If you want to avoid this kind of situation, save the citations by clicking on the star next to the word Save, and then use those citations to search MNLINK or eLibraryMN.
Google Scholar is best (in my opinion) when used in conjunction with other repositories. That way, you'll get access to a wider range of information.
Google Scholar shouldn't be the only place you search. This resource explains why.
One aspect of Google Scholar that is important to note: Google Scholar links out to various repositories, many that are legal, and some that aren't. There may be some ethical decisions to make when conducting your research primarily in Google Scholar. If you want to avoid this kind of situation, save the citations by clicking on the star next to the word Save, and then use those citations to search MNLINK or eLibraryMN.
Google Scholar is best (in my opinion) when used in conjunction with other repositories. That way, you'll get access to a wider range of information.
Go to https://scholar.google.com/
There's no need to set up a Google account if you don't already have one.
There's no need to set up a Google account if you don't already have one.
Google Scholar searches just like Google and connects to existing Google accounts, if you want to be able to save citations/articles or set up a profile that connects to any publications you've authored.
The advanced search (click on the menu icon marked by the number 1 in the graphic) and additional filters are limited compared to other research platforms, but it's a great place to search if you're looking for open access materials, which sometimes aren't as well indexed in subscription platforms like EBSCO and ProQuest.
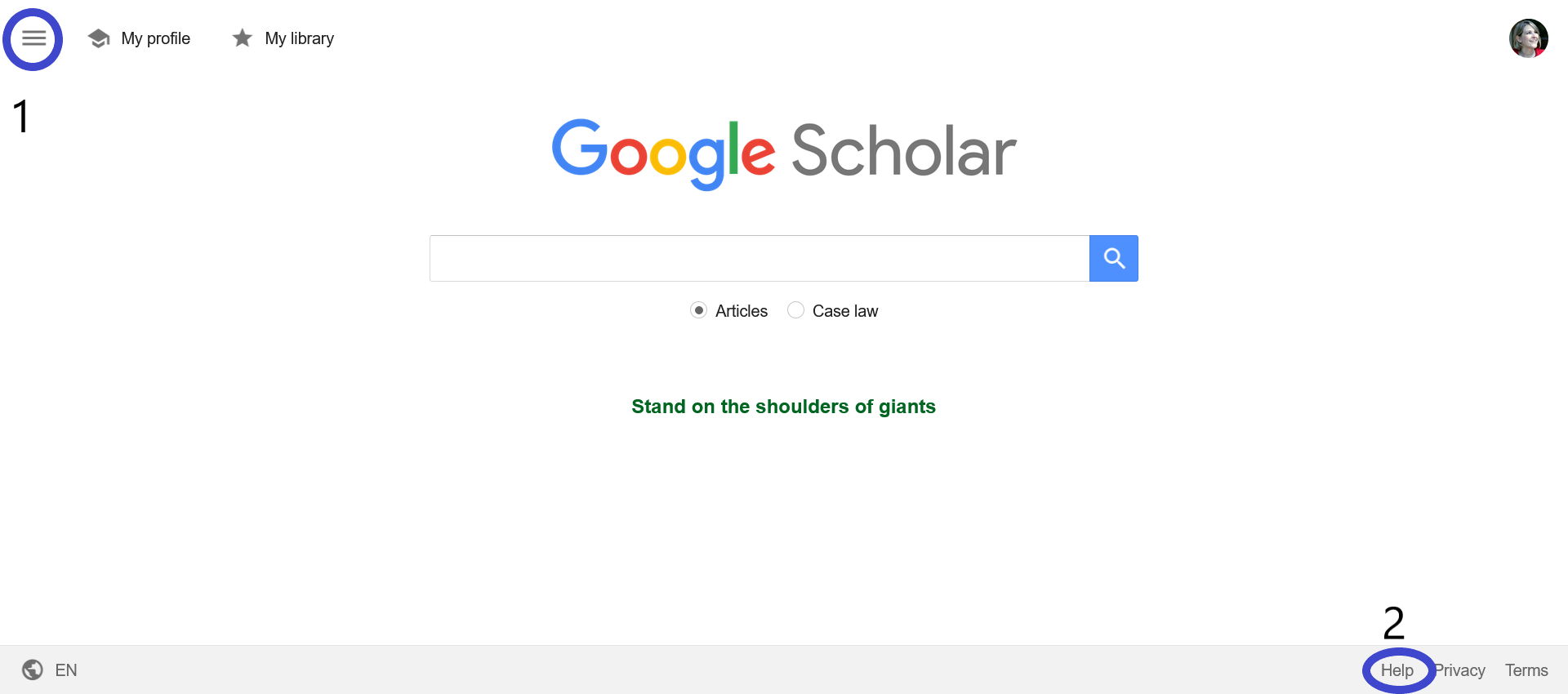
If you're looking for more information and tips about Google Scholar, click on Help at the bottom right, marked by the number 2 on the graphic.
The advanced search (click on the menu icon marked by the number 1 in the graphic) and additional filters are limited compared to other research platforms, but it's a great place to search if you're looking for open access materials, which sometimes aren't as well indexed in subscription platforms like EBSCO and ProQuest.

If you're looking for more information and tips about Google Scholar, click on Help at the bottom right, marked by the number 2 on the graphic.
Some reminders about effective searching:
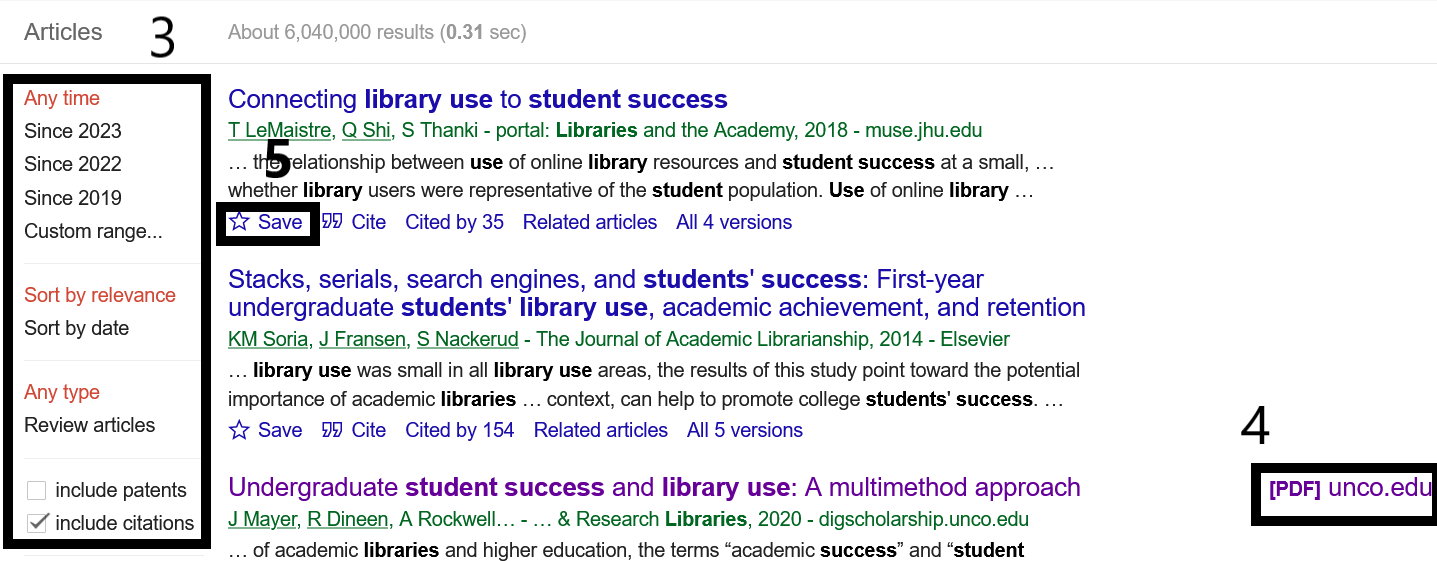
And, if you see a result that has a link to the article, click it to access it, as shown by the number 4 on the graphic.
- Use keywords in combination to get narrower results. Student success higher education is more specific than student success.
- If you are searching for a specific phrase, put quotation marks around it to search it as a unit (e.g. "student success")
- Good searching can take time.
- Different disciplines use different terminology- make notes when you find words and phrases that seem to hit the mark.
- Take advantage of the filters on the left side, shown in the graphic marked with a 3.

And, if you see a result that has a link to the article, click it to access it, as shown by the number 4 on the graphic.